Importance and use of correlational research
Table Of Content
For one, the data is not always reliable—particularly if the survey questions are poorly written or the overall design or delivery is weak. Data is also affected by specific faults, such as unrepresented or underrepresented samples. If researchers need to gather a large amount of data in a short period of time, a survey is likely to be the fastest, easiest, and cheapest option. However, this does not mean that researchers will get reliable data from watching the variables, or that the information they gather will be free from bias.
Archival Research
In correlational research, it is not possible to establish the fact, what causes what. It is a misconception that a correlational study involves two quantitative variables. This is true independent of whether the variables are quantitative or categorical. A correlation coefficient is a statistical measure that quantifies the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
How to analyse correlational data
Social Psychology Research Methods - Verywell Mind
Social Psychology Research Methods.
Posted: Mon, 06 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Correlations that are a result not of the two variables being measured, but rather because of a third, unmeasured, variable that affects both of the measured variables. Ethnography is a type of research where a researcher observes the people in their natural environment. Instead of collecting new data, you can use the existing data in your research if it fulfills your research requirements. Generally, previous studies or theories, records, documents, and transcripts are used as the primary source of information. For example, being educated might negatively correlate with the crime rate when an increase in one variable leads to a decrease in another and vice versa. It only means that a lack of education and crime is believed to have a common reason – poverty.

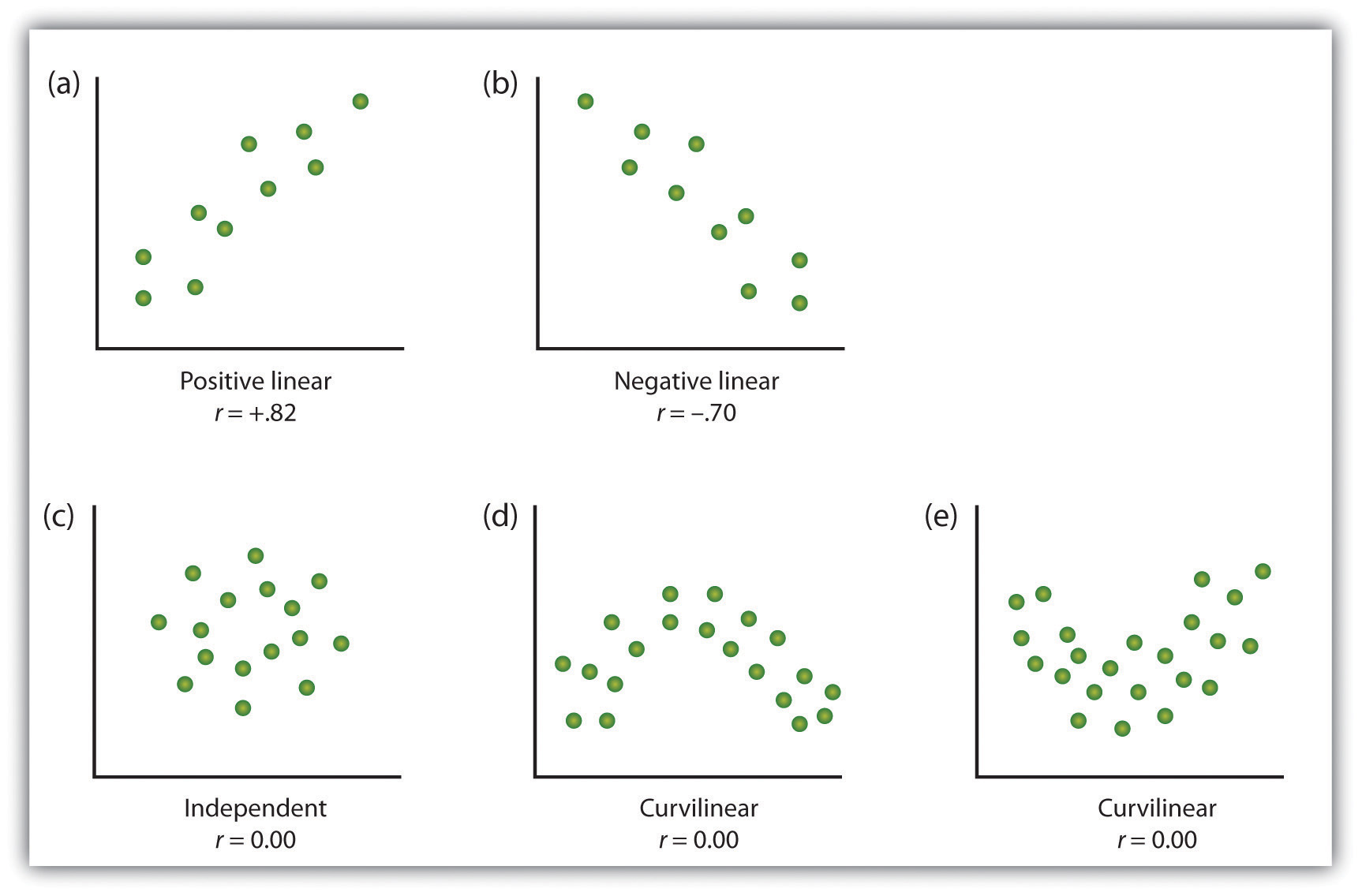
Scatterplots
In some cases, it might be the only method available to researchers; for example, if lab experimentation would be precluded by access, resources, or ethics. It might be preferable to not being able to conduct research at all, but the method can be costly and usually takes a lot of time. A correlation is usually tested for two variables at a time, but you can test correlations between three or more variables. A correlation reflects the strength and/or direction of the association between two or more variables.
Qualitative Research Methods

However, you can carry out correlational research to find out if victims of domestic violence suffer brain hemorrhage more than non-victims. Naturalistic observation has revealed that bowlers tend to smile when they turn away from the pins and toward their companions, suggesting that smiling is not purely an expression of happiness but also a form of social communication. By Kendra Cherry, MSEdKendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
This is because correlation merely describes the degree to which two variables co-vary; it does not establish a cause-and-effect relationship between them. The 3 methods of data collection in correlational research are naturalistic observation method, archival data method, and the survey method. The purpose of correlational research is to examine the relationship between two or more variables. Correlational research allows researchers to identify whether there is a relationship between variables, and if so, the strength and direction of that relationship.
For example, counting the number of people named Virginia who live in various states based on Social Security records is relatively straightforward. In the late 1980s, Peterson and his colleagues reviewed the men’s questionnaire responses to obtain a measure of explanatory style—their habitual ways of explaining bad events that happen to them. More pessimistic people tend to blame themselves and expect long-term negative consequences that affect many aspects of their lives, while more optimistic people tend to blame outside forces and expect limited negative consequences. To obtain a measure of explanatory style for each participant, the researchers used a procedure in which all negative events mentioned in the questionnaire responses, and any causal explanations for them, were identified and written on index cards. These were given to a separate group of raters who rated each explanation in terms of three separate dimensions of optimism-pessimism. These ratings were then averaged to produce an explanatory style score for each participant.
For example, people in Canada and Sweden covered 60 feet in just under 13 seconds on average, while people in Brazil and Romania took close to 17 seconds. When one or both variables have a limited range in the sample relative to the population, making the value of the correlation coefficient misleading. A graph that presents correlations between two quantitative variables, one on the x-axis and one on the y-axis.
Frequently asked questions about correlational research
Controlled experiments establish causality, whereas correlational studies only show associations between variables. In correlational research, there’s limited or no researcher control over extraneous variables. Even if you statistically control for some potential confounders, there may still be other hidden variables that disguise the relationship between your study variables. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient, also known as Pearson’s r, is commonly used for assessing a linear relationship between two quantitative variables. A statistic that measures the strength of a correlation between quantitative variables.
Figure 6.3 Scatterplot Showing a Hypothetical Positive Relationship Between Stress and Number of Physical Symptoms. The circled point represents a person whose stress score was 10 and who had three physical symptoms. A person might answer a particular way to try to please the researchers or to try to control how the researchers perceive them (such as trying to make themselves "look better").
Naturalistic observation is a correlational research methodology that involves observing people’s behaviors as shown in the natural environment where they exist, over a period of time. It is a type of research-field method that involves the researcher paying closing attention to natural behavior patterns of the subjects under consideration. Observational studies involve observing and recording the behavior of participants in natural settings. Researchers can use observational studies to examine the relationships between variables such as social interactions, group dynamics, and communication patterns.
They have made it difficult to design rcts with sufficient sample size and long-term follow-up to account for all the variability this phenomenon entails. Also rcts are intended to test the efficacy of an intervention in a restricted sample of subjects under ideal settings. They have limited generalizability to the population at large in routine settings (Fleurence, Naci, & Jansen, 2010). As such, correlational studies, especially those involving the use of routinely collected ehr data from the general population, have become viable alternatives to rcts.
For example, wealth and patience can be variables under zero correlational research because they are statistically independent. Correlational research is a type of research method that involves observing two variables in order to establish a statistically corresponding relationship between them. The aim of correlational research is to identify variables that have some sort of relationship do the extent that a change in one creates some change in the other. There are two common situations in which the value of Pearson’s r can be misleading.
You collect data on loneliness using three different measures, including the new scale, and test the degrees of correlations between the different measurements. An approach to data collection that involves observing people’s behaviour in the environment in which it typically occurs. Another approach to correlational research is the use of archival data, which are data that have already been collected for some other purpose. A meta-analysis is a formal, epidemiological, quantitative study design that uses statistical methods to generalise the findings of the selected independent studies. Archival information is the data that has been previously collected by doing similar kinds of research.
Comments
Post a Comment